What Is Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is one of the essential vitamins needed for good health. It is also known as ascorbic acid and it is a water-soluble vitamin, besides vitamin B. It is required for growth and development and it helps the body in absorbing iron from the diet. Vitamin C aids in controlling infections and wound healing. It is a strong antioxidant that protects the body from harmful free radicals. It is needed for making collagen, which is a fibrous protein in connective tissue present in different tissues of the body like nerves, bone, cartilage, blood, etc. Vitamin C also acts in the synthesis of many hormones and neurotransmitters found in the brain and nerves.
As the human body cannot synthesize or store vitamin C so it has to be regularly included in the diet. Mostly its requirement is fulfilled by the food. One need not have to worry about its intake as long as a person is taking a healthy and balanced diet consisting of adequate quantities of fruits and vegetables.
What Are the Sources of Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is the content of many commonly eaten foods, especially fruits and vegetables. It can be best obtained as raw or in uncooked form. Cooking or storing them for a longer duration can decrease their vitamin C content.
Some of the best sources of Vitamin C are:
-
Citrus fruits like oranges, kiwi, lemon, and grapefruit.
-
Bell peppers - green and red.
-
Strawberries.
-
Kale.
-
Tomatoes.
-
Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, etc.
-
Potatoes.
Orange juice is regarded as a rich source of vitamin C. However, freshly squeezed orange juice is preferred over packed orange juice as it does not contain preservatives. It also has around 96 mg of vitamin C, whereas the store-bought orange juice only contains about 65 mg of it.
How Much Vitamin C Should I Take Every Day?
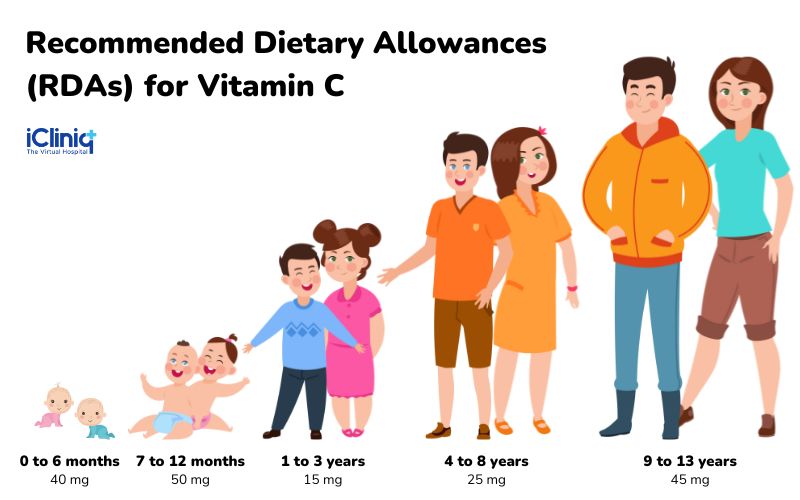
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for adult (19 years and above) men is 90 mg per day and for adult women is 75 mg daily. For pregnant and lactating women, the quantity has been increased to 85 mg and 120 mg per day, respectively. Though an intake of more than 35 mg is suggested (up to 120 mg) for smokers, because of vitamin C deprivation, it would be ideal to cessate or limit the smoking habit as it can result in ascorbic acid deficiency.
The RDA is much less than that provided by one supplement, so taking supplements is not required, which are of 500 to 1000 mg usually.
The upper-level tolerable intake (UL) is the maximum daily intake that is unlikely to cause deleterious outcomes for health. For vitamin C, the UL is 2000 mg per day. Consuming more than this amount may lead to gastrointestinal issues. Only in specific conditions, under medical supervision, or in controlled clinical trials, quantities higher than UL can be taken.
What Are the Manifestations of Vitamin C Deficiency?
Vitamin C deficiency is common in developing countries compared to developed ones. However, it may occur due to a restricted diet that contributes less than 10 mg of vitamin C daily for one month or a longer period. It is also caused because of smoking or long-term exposure to passive smoke, drug intake, and alcohol abuse.
The following manifestations are of vitamin C deficiency:
-
Scurvy is caused by severe vitamin C deficiency. It results in loss of collagen and hence, weakened connective tissue.
-
Skin spots occur due to bleeding and bruising of broken blood vessels.
-
Swollen or bleeding gums leading to tooth loss.
-
Periodontal disease or tooth-related problems.
-
Hair loss.
-
Delayed wound healing of oral mucous membrane and skin.
-
Fatigue, malaise.
-
Weight gain.
-
Swollen and painful joints.
-
Weak bones.
-
Rough and bumpy skin.
-
Spoon-shaped fingernails.
-
Low mood.
-
Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation.
-
Iron-deficiency anemia due to decreased absorption of nonheme iron.
How Much of Vitamin C Is Too Much?
Although the UL for vitamin C is 2000 mg daily yet, it is very dubious that a person will ever consume more than 2,000 mg in a day through diet. It is only by taking supplements that contain 500 to 1,000 mg of vitamin C that overdose occurs.
An overdose of vitamin C can never be life threatening, however daily intake of large vitamin C dosage can result in:
-
Diarrhea.
-
Nausea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Abdominal pain and cramps.
-
Headache.
-
Fatigue.
-
Fever.
-
Renal stones.
-
Irritability.
-
Nose bleeding.
-
Menstrual abnormalities in females.
-
Weight loss.
-
Disturbed mental health.
-
Seizures.
-
Muscle pain and weakness.
-
Bone fractures.
-
Dry mucous membrane.
-
Per-rectal bleeding.
As vitamin C is water-soluble in nature, it is expelled by the body as urine and feces if its toxicity occurs. However, critical adverse effects of vitamin C toxicity are rare.
What Are the Possible Interactions With Vitamin C Supplements?
Vitamin C supplements interact with several drugs. Their combinations should be avoided. Some of them are as follows:
-
Vitamin C and Aluminum: Vitamin C can increase the absorption of aluminum in the body. Aluminum is found in antacids so vitamin C supplements should be taken two hours before or four hours after taking antacids.
-
Vitamin C and Estrogen: Vitamin C decreases the elimination of estrogen from the body so vitamin C should not be taken along with estrogen formulations. This combination might increase the effects and adverse effects of estrogen hormone.
-
Vitamin C and Fluphenazine: Increased amounts of vitamin C might decrease the effectiveness of Fluphenazine in the body.
-
Vitamin C and Cancer Drugs (alkylating agents): Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and it might decrease the efficacy of some cancer medications, including anti-cancer drugs. A patient on cancer medications should take vitamin C supplements only on the recommendation of a healthcare provider.
-
Vitamin C and Warfarin: Warfarin is an anticoagulant. High amounts of vitamin C might decrease the efficacy of Warfarin thus increasing the risk of clotting. The dose of Warfarin should be adjusted accordingly.
-
Vitamin C and Levothyroxine: Vitamin C affects the absorption and elimination of Levothyroxine in the body so vitamin C supplements can increase Levothyroxine levels in the body and also its effectiveness and side effects.
Conclusion:
Vitamin C is an inseparable part of a healthy diet but it has both pros and cons. It should be consumed regularly yet, in the recommended amounts to make the most of its benefits and prevent its adverse effects. Care should be taken to prevent its complications too.









