Introduction:
Exercise and regular physical activity can reduce the risk of many diseases, including cardiovascular diseases. Physiotherapy (PT) can help in regulating the blood flow and proper functioning of the heart. A sedentary lifestyle not only leads to obesity but also is an underlying cause of the majority of diseases.
Why Should Physiotherapy Be Done?
-
Physiotherapy is done to restore movement and function in an individual who is affected by injury, illness, or disability through non-surgical methods.
-
It is more like an exercise and targets the well-being of the individual.
-
It also helps build back strength in the body after a major injury.
-
Physiotherapy involves transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), magnetic therapy, stretches, and exercises.
What Are Cardiovascular Diseases?
Cardiovascular diseases are a wide range of diseases that affect the heart and its vessels. They are the leading cause of death around the globe. Some cardiovascular diseases include hypertension, ischemic heart disease, angina, myocardial infarction, dyspnea, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
When to Do Physical Therapy?
An exercise is also a form of stress that can loaden the heart with extra work. Heart rate, stroke volume, and systolic blood pressure increase during exercise. So, the cardiac output increases, resulting in improved blood flow to the muscles we are working on. This is how endurance training is done to improve cardiorespiratory fitness.
Can Physiotherapy Be Done After Cardiac Surgery?
-
Physiotherapy is done on patients having cardiovascular problems after risk stratification is done.
-
After the concerned doctor approves of physiotherapy, many kinds of treatments are given, like breathing exercises, incentive spirometry, and huffing and coughing.
-
The treatment varies according to the disease severity. Physiotherapy even helps to prevent some cardiovascular problems. After assessing the risk factors, individualized treatment plans are given by physiotherapists to prevent heart diseases.
-
Right after heart surgery, the cardiorespiratory function is impaired, and patients are advised to move and do some breathing exercises. This is called early mobilization, and it is done to reduce post-operative complications, bring back the impaired cardiorespiratory function, reduce the length of hospital stay and get back to routine.
Will Physical Inactivity Cause Cardiovascular Problems?
Moderate forms of exercise are always advised to have good heart health. Being in bedrest is the sickest state according to the health-activity spectrum. Bedrest is common in stroke, coma, spinal injury, and old age. Other than that, even lower limb injuries and abnormalities can immobilize patients. Immobilization, in turn, causes muscular atrophy, leading to wasting those muscles and weakening. Also, there will be declined heart function and loss in bone density if the period is prolonged.
How Is Physiotherapy Done?
Physiotherapy is started only after conducting the fitness test. Some cardiac patients are contraindicated for this test. The fitness test is done in physiotherapy clinics and fitness specialties and is not a diagnostic procedure in a lab setting. This is usually done on a treadmill, and blood pressure and ECG (electrocardiogram) are recorded. Any exercise given to the individual is unique and has these five components:
-
Frequency.
-
Intensity.
-
Time.
-
Type.
-
Rate of progression.
Based on the patient’s coping skills and ability, the exercises are customized by the therapist.
What Is Cardiac Rehabilitation?
It is done for people with heart disease or those who have recovered from heart surgeries to restore health and educate and train them for betterment. Cardiac rehabilitation programs have many types of exercises. Aerobic exercises are low-intensity exercises, and they use up oxygen for energy. Anaerobic exercises are high-intensity exercises, and they do not require oxygen. Cardiac rehabilitation is done immediately after surgery in some patients.
Indications:
Cardiac rehabilitation is indicated in the following cardiac patients:
-
Patients who recently had myocardial infarction are stable.
-
Patients with acute coronary artery syndrome.
-
Patients with stable CHF (congestive heart failure).
-
Patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass surgery.
-
Patients who have undergone heart transplantation.
-
Patients who have chronic stable angina.
-
Patients who have undergone valvular surgery.
-
Patients with cardiomyopathy.
-
Patients who have had cerebral vascular disease.
Contraindications:
The following patients are contraindicated for cardiac rehabilitation program:
-
Patients who have unstable angina.
-
Patients who have uncontrolled arrhythmias.
-
Patients who have third-degree atrioventricular block and with no pacemaker.
-
Patients who have had embolism recently.
-
Patients with uncontrolled diabetes.
-
Patients with acute myocarditis.
-
Patients who have severe orthopedic problems.
-
Patients who have other metabolic problems such as hypovolemia and acute thyroiditis.
-
Patients who have thrombophlebitis.
-
Patients with decompensated congestive heart failure.
-
Patients with acute systemic illness or fever.
What Are the Phases of Cardiac Rehabilitation?
Cardiac rehabilitation consists of three phases:
1. Phase One: The clinical phase begins by assessing the patient’s ability to perform basic exercises. It is done after being diagnosed with a heart problem. Physiotherapists and nurses teach patients various exercises to restore form and function. In addition, they teach ADLs (activities of daily living) like combing hair, sitting on a chair, dressing up, etc. The rehabilitation team also assesses whether the patient needs any assistive devices.
2. Phase Two: This phase is outpatient cardiac rehabilitation. After discharge and the cardiologist’s consent, this phase begins. It can last up to 12 weeks and as short as six weeks. In this phase, the patient is engaged in vigorous training followed by rest. This is done to make the patient return back to a normal routine.
3. Phase Three: This phase lasts around 6 to 12 weeks and is a structured exercise program component. It involves doing exercises that improve flexibility and strengthening. Risk stratification is done during this process.
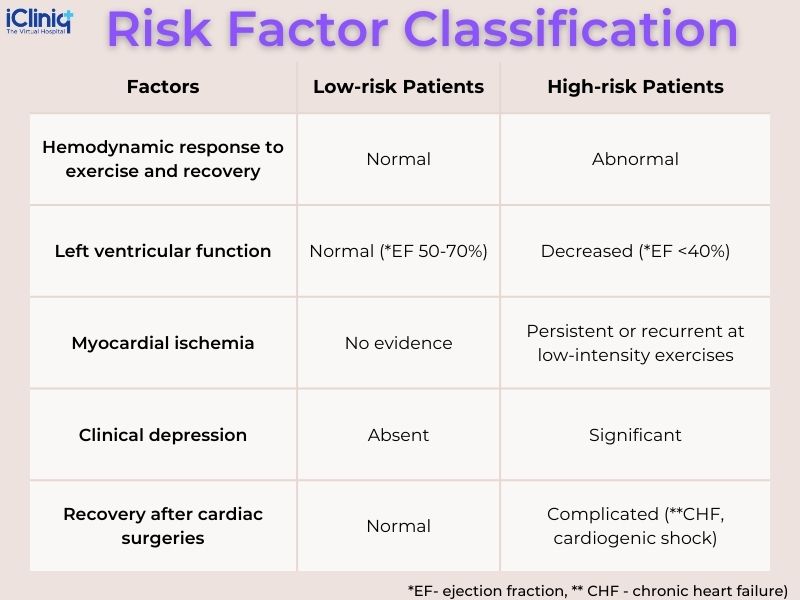
Risk Factor Classification:
4. Phase Four: In this phase, the patients should be transferred to a long-term rehabilitation program if they are medically stable. They can do aerobic and strengthening exercises as they wish in this phase.
Conclusion:
Patients who have had cardiac problems or have undergone surgery can return to their normal physical activity after undergoing proper physiotherapy and rehabilitation. Pre and post-surgery physiotherapy is important for restoring the normal health of the individual.









